SpringMVC-zero
读书不作儒生酸,跃马西入金城关。
SpringMVC
zero: 记录一些零碎的知识点
数据传输
请求参数
URL传参
- url 传参过程中,controller接收的有多实体类,并且实体类间含有同名字段
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/sameName")
public String test1(User user, Book book){
return user.toString() + book.toString();
}
}
@Data
public class User {
private String name;
private String password;
}
@Data
public class Book {
private String id;
private String name;
}
springmvc进行转换时会对同名的字段都赋值

当同一个字段有多个值时会用逗号分隔

如何让mvc为不同的实体类中相同的字段赋不同的值? 参阅 ControllerAdvice 的介绍及三种用法
- todo
注解
@ControllerAdvice
首先,
ControllerAdvice本质上是一个Component,因此也会被当成组件扫描。

然后,我们来看一下此类的注释:
这个类是为那些声明了(
@ExceptionHandler、@InitBinder或@ModelAttribute注解修饰的)方法的类而提供的专业化的@Component, 以供多个Controller类所共享。说白了,就是aop思想的一种实现,你告诉我需要拦截规则,我帮你把他们拦下来,具体你想做更细致的拦截筛选和拦截之后的处理,你自己通过
@ExceptionHandler、@InitBinder或@ModelAttribute这三个注解以及被其注解的方法来自定义。

初定义拦截规则:
ControllerAdvice提供了多种指定Advice规则的定义方式,默认什么都不写,则是Advice所有Controller,当然你也可以通过下列的方式指定规则 比如对于String[] value() default {}, 写成@ControllerAdvice("org.my.pkg")或者@ControllerAdvice(basePackages="org.my.pkg"), 则匹配org.my.pkg包及其子包下的所有Controller,当然也可以用数组的形式指定,如:@ControllerAdvice(basePackages={"org.my.pkg", "org.my.other.pkg"}), 也可以通过指定注解来匹配,比如我自定了一个@CustomAnnotation注解,我想匹配所有被这个注解修饰的Controller, 可以这么写:@ControllerAdvice(annotations={CustomAnnotation.class})还有很多用法,这里就不全部罗列了。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface ControllerAdvice {
@AliasFor("basePackages")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
Class<?>[] assignableTypes() default {};
Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotations() default {};
}
1.处理全局异常
@ControllerAdvice配合@ExceptionHandler实现全局异常处理

用于在特定的处理器类、方法中处理异常的注解

接收Throwable类作为参数,我们知道Throwable是所有异常的父类,所以说,可以自行指定所有异常
比如在方法上加:
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class),则表明此方法处理
IllegalArgumentException类型的异常,如果参数为空,将默认为方法参数列表中列出的任何异常(方法抛出什么异常都接得住)。下面的例子:处理所有
IllegalArgumentException异常,域中加入错误信息errorMessage并返回错误页面error
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class)
public ModelAndView handleException(IllegalArgumentException e){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("error");
modelAndView.addObject("errorMessage", "参数不符合规范!");
return modelAndView;
}
}
2.预设全局数据
@ControllerAdvice配合@ModelAttribute预设全局数据我们先来看看
ModelAttribute注解类的源码
/**
* Annotation that binds a method parameter or method return value
* to a named model attribute, exposed to a web view. Supported
* for controller classes with {@link RequestMapping @RequestMapping}
* methods.
* 此注解用于绑定一个方法参数或者返回值到一个被命名的model属性中,暴露给web视图。支持在
* 在Controller类中注有@RequestMapping的方法使用(这里有点拗口,不过结合下面的使用介绍
* 你就会明白的)
*/
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ModelAttribute {
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
boolean binding() default true;
}
实际上这个注解的作用就是,允许你往
Model中注入全局属性(可以供所有Controller中注有@Request Mapping的方法使用),value和name用于指定 属性的key,binding表示是否绑定,默认为true。具体使用方法如下:
-
全局参数绑定
- 方式一:
@ControllerAdvice public class MyGlobalHandler { @ModelAttribute public void presetParam(Model model){ model.addAttribute("globalAttr","this is a global attribute"); } }这种方式比较灵活,需要什么自己加就行了,加多少属性自己控制
- 方式二:
@ControllerAdvice public class MyGlobalHandler { @ModelAttribute() public Map<String, String> presetParam(){ Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); map.put("key1", "value1"); map.put("key2", "value2"); map.put("key3", "value3"); return map; } }这种方式对于加单个属性比较方便。默认会把返回值(如上面的map)作为属性的value,而对于key有两种指定方式:
- 当
@ModelAttribute()不传任何参数的时候,默认会把返回值的字符串值作为key,如上例的key则是 ”map”(值得注意的是,不支持字符串的返回值作为key)。 - 当
@ModelAttribute("myMap")传参数的时候,则以参数值作为key,这里key则是 ”myMap“。
-
全局参数使用
@RestController public class AdviceController { @GetMapping("methodOne") public String methodOne(Model model){ Map<String, Object> modelMap = model.asMap(); return (String)modelMap.get("globalAttr"); } @GetMapping("methodTwo") public String methodTwo(@ModelAttribute("globalAttr") String globalAttr){ return globalAttr; } @GetMapping("methodThree") public String methodThree(ModelMap modelMap) { return (String) modelMap.get("globalAttr"); } }这三种方式大同小异,其实都是都是从
Model中存储属性的Map里取数据。
3.请求参数预处理
@ControllerAdvice配合@InitBinder实现对请求参数的预处理再次之前我们先来了解一下
@IniiBinder,先看一下源码,我会提取一些重要的注释进行浅析
/**
* Annotation that identifies methods which initialize the
* {@link org.springframework.web.bind.WebDataBinder} which
* will be used for populating command and form object arguments
* of annotated handler methods.
* 粗略翻译:此注解用于标记那些 (初始化[用于组装命令和表单对象参数的]WebDataBinder)的方法。
* 原谅我的英语水平,翻译起来太拗口了,从句太多就用‘()、[]’分割一下便于阅读
*
* Init-binder methods must not have a return value; they are usually
* declared as {@code void}.
* 粗略翻译:初始化绑定的方法禁止有返回值,他们通常声明为 'void'
*
* <p>Typical arguments are {@link org.springframework.web.bind.WebDataBinder}
* in combination with {@link org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest}
* or {@link java.util.Locale}, allowing to register context-specific editors.
* 粗略翻译:典型的参数是`WebDataBinder`,结合`WebRequest`或`Locale`使用,允许注册特定于上下文的编辑
* 器。
*
* 总结如下:
* 1. @InitBinder 标识的方法的参数通常是 WebDataBinder。
* 2. @InitBinder 标识的方法,可以对 WebDataBinder 进行初始化。WebDataBinder 是 DataBinder 的一
* 个子类,用于完成由表单字段到 JavaBean 属性的绑定。
* 3. @InitBinder 标识的方法不能有返回值,必须声明为void。
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface InitBinder {
/**
* The names of command/form attributes and/or request parameters
* that this init-binder method is supposed to apply to.
* <p>Default is to apply to all command/form attributes and all request parameters
* processed by the annotated handler class. Specifying model attribute names or
* request parameter names here restricts the init-binder method to those specific
* attributes/parameters, with different init-binder methods typically applying to
* different groups of attributes or parameters.
* 粗略翻译:此init-binder方法应该应用于的命令/表单属性和/或请求参数的名称。默认是应用于所有命 * 令/表单属性和所有由带注释的处理类处理的请求参数。这里指定模型属性名或请求参数名将init-binder * 方法限制为那些特定的属性/参数,不同的init-binder方法通常应用于不同的属性或参数组。
* 我至己都理解不太理解这说的是啥呀,我们还是看例子吧
*/
String[] value() default {};
}
我们来看看具体用途,其实这些用途在
Controller里也可以定义,但是作用范围就只限当前Controller,因此下面的例子我们将结合ControllerAdvice作全局处理。
-
参数处理
@ControllerAdvice public class MyGlobalHandler { @InitBinder public void processParam(WebDataBinder dataBinder){ /* * 创建一个字符串微调编辑器 * 参数{boolean emptyAsNull}: 是否把空字符串("")视为 null */ StringTrimmerEditor trimmerEditor = new StringTrimmerEditor(true); /* * 注册自定义编辑器 * 接受两个参数{Class<?> requiredType, PropertyEditor propertyEditor} * requiredType:所需处理的类型 * propertyEditor:属性编辑器,StringTrimmerEditor就是 propertyEditor的一个子类 */ dataBinder.registerCustomEditor(String.class, trimmerEditor); //同上,这里就不再一步一步讲解了 binder.registerCustomEditor(Date.class, new CustomDateEditor(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"), false)); } }这样之后呢,就可以实现全局的实现对
Controller中RequestMapping标识的方法中的所有String和Date类型的参数都会被作相应的处理。Controller:
@RestController public class BinderTestController { @GetMapping("processParam") public Map<String, Object> test(String str, Date date) throws Exception { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("str", str); map.put("data", date); return map; } }测试结果:
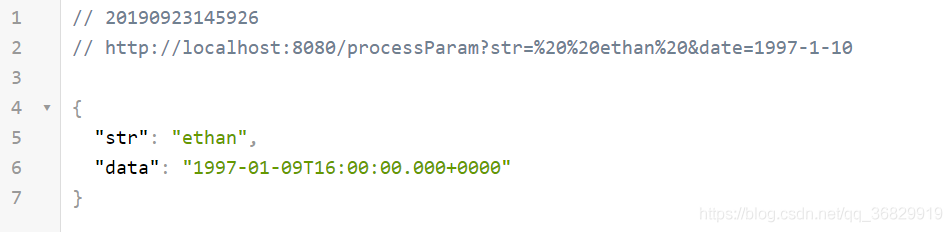
我们可以看出,
str和date这两个参数在进入Controller的test的方法之前已经被处理了,str被去掉了两边的空格(%20在Http url 中是空格的意思),String类型的1997-1-10被转换成了Date类型。 -
参数绑定
参数绑定可以解决特定问题,那么我们先来看看我们面临的问题
class Person { private String name; private Integer age; // omitted getters and setters. } class Book { private String name; private Double price; // omitted getters and setters. } @RestController public class BinderTestController { @PostMapping("bindParam") public void test(Person person, Book book) throws Exception { System.out.println(person); System.out.println(book); } }我们会发现
Person类和Book类都有name属性,那么这个时候就会出先问题,它可没有那么只能区分哪个name是哪个类的。因此@InitBinder就派上用场了:@ControllerAdvice public class MyGlobalHandler { /* * @InitBinder("person") 对应找到@RequstMapping标识的方法参数中 * 找参数名为person的参数。 * 在进行参数绑定的时候,以‘p.’开头的都绑定到名为person的参数中。 */ @InitBinder("person") public void BindPerson(WebDataBinder dataBinder){ dataBinder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("p."); } @InitBinder("book") public void BindBook(WebDataBinder dataBinder){ dataBinder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("b."); } }因此,传入的同名信息就能对应绑定到相应的实体类中:
p.name -> Person.name b.name -> Book.name
还有一点注意的是如果
@InitBinder("value")中的value值和Controller中@RequestMapping()标识的方法的参数名不匹配,则就会产生绑定失败的后果,如:@InitBinder(“p”)、@InitBinder(“b”)
public void test(Person person, Book book)
上述情况就会出现绑定失败,有两种解决办法
第一中:统一名称,要么全叫
p,要么全叫person,只要相同就行。第二种:方法参数加
@ModelAttribute,有点类似@RequestParam@InitBinder(“p”)、@InitBinder(“b”)
public void test(@ModelAttribute(“p”) Person person, @ModelAttribute(“b”) Book book)
参数传递与接收
1. from-data
-
就是http请求中的multipart/form-data,它会将表单的数据处理为一条消息,以标签为单元,用分隔符分开。
既可以上传键值对,也可以上传文件。当上传的字段是文件时,会有Content-Type来表明文件类型;content-disposition ,用来说明字段的一些信息;
- 由于有boundary 隔离,所以multipart/form-data既可以上传文件,也可以上传键值对,它采用了键值对的方式,所以可以上传多个文件。
2.x-www-form-urlencoded
- 就是application/x-www-from-urlencoded,会将表单内的数据转换为键值对,比如,username=张三
Content-Type

3.raw
- 以上传任意格式的文本,可以上传text、json、xml、html等
- content-type= text/html(HTML 文档);text/plain(纯文本);text/css(CSS 样式表);application/json (json字符串)
4.binary
- 相当于Content-Type:application/octet-stream,从字面意思得知,只可以上传二进制数据,通常用来上传文件,由于没有键值,所以,一次只能上传一个文件。
MULTIPART/FORM-DATA与X-WWW-FORM-URLENCODED区别
- multipart/form-data:既可以上传文件等二进制数据,也可以上传表单键值对,
- x-www-form-urlencoded:只能上传键值对,并且键值对都是间隔分开的,只是最后会转化为一条信息。
@RequestParam
- 用来处理(前端)Content-Type: 为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded或者form-data编码的内容
- 该注解有两个属性: value、required; value用来指定要传入值的id名称,required用来指示参数是否必须绑定;
@RequestBody
- 该注解常用来处理Content-Type: 不是application/x-www-form-urlencoded编码的内容,例如application/json, application/xml等;
- 前端规定的是raw方式,那么就需要使用@RequestBody接收参数,注意这里Headers里需要以application/json作为Content-type
what’s your Problems
版权声明:如无特别声明,本站收集的文章归 HuaJi66/Others 所有。 如有侵权,请联系删除。
联系邮箱: GenshinTimeStamp@outlook.com
本文标题:《 SpringMVC-zero 》

